Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Module
CME credit available from Harvard Medical School through 2025.
Published materials
- CME-CE activity detail page
- Summary Brochure
- Evidence Document
- Reference Card
- Patient Brochure
- Patient Tear-off Sheet
The goal of this educational program is to provide practitioners with up-to-date evidence-based treatment recommendations for type 2 diabetes, including individualized glycemic target, choice of glucose-lowering medications based on cardiovascular outcome data, and treatment simplification to avoid hypoglycemia.
Over 96 million Americans have prediabetes. Patients with prediabetes can prevent or delay the progression to diabetes through lifestyle interventions. Changes to diet and exercise are very effective for older adults. The Diabetes Prevention Program can help patients implement and sustain these lifestyle modifications. More information available at AlosaHealth.org/Prediabetes.
Over 37 million Americans have diabetes. Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 90-95% of diabetes cases, is most prevalent in people age 65 and over.1 These patients require a personalized approach to treatment. Goals of treatment have expanded beyond controlling HbA1c. Two goals now drive treatment decisions:
1. Use medications that reduce complications from diabetes
2. Control blood glucose
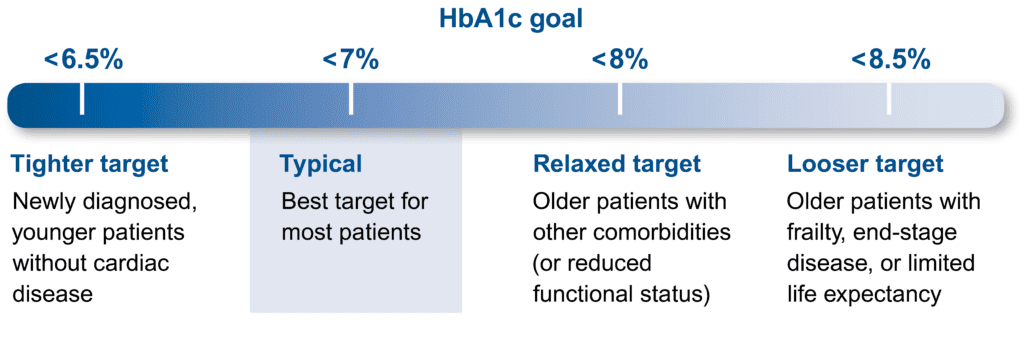
For most healthy, younger adults, lower HbA1c targets are best, but for older adults with increasingly complex health concerns a higher goal may be more better.
Individualize treatment goals for older patients with diabetes2
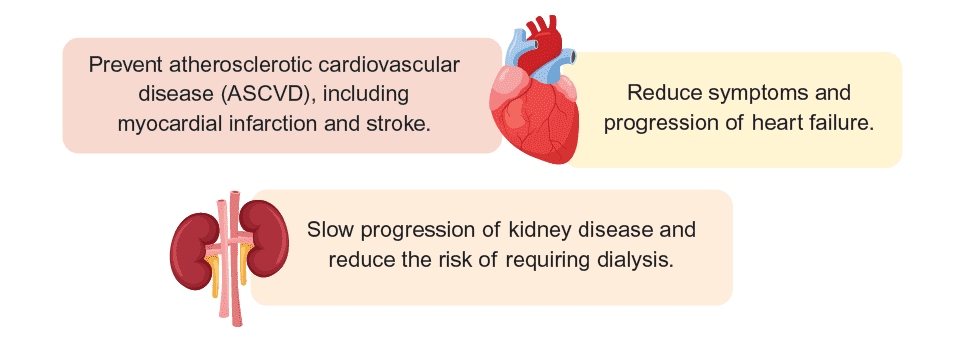
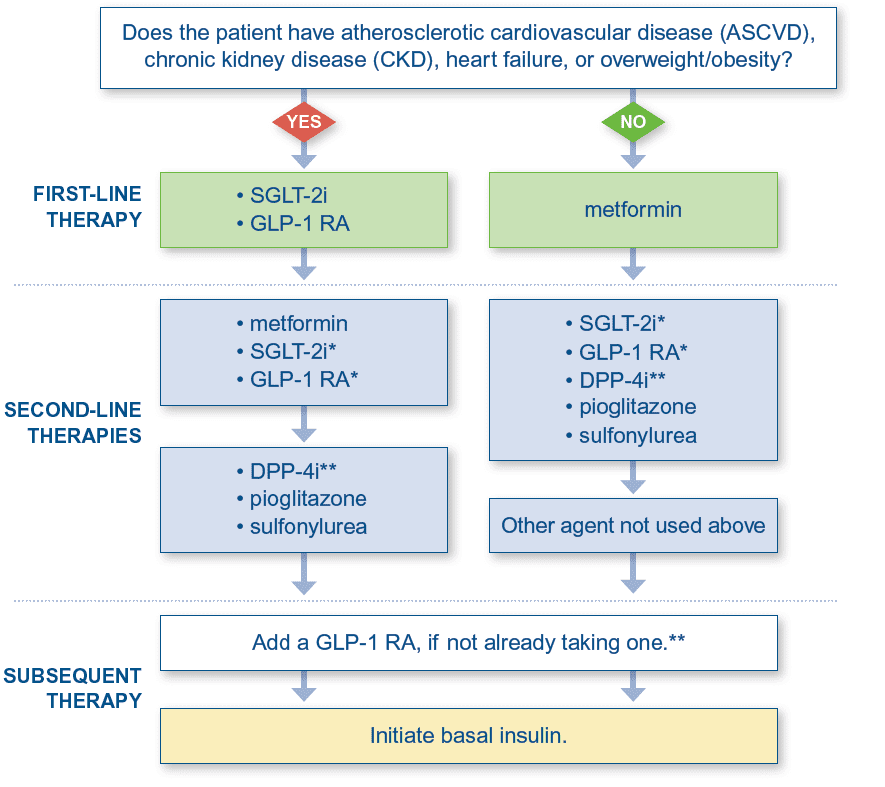
Treatment guidelines have shifted from starting metformin in all patients with diabetes to selecting treatment based on the presence of comorbidities, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), heart failure, or overweight/obesity. Metformin should be initiated in patients without these conditions.2
Treatment paths for patients who are not at HbA1c goal
* SGLT-2is and GLP-1 RAs can be used in combination to address specific comorbidities, but this approach has not yet been formally evaluated in a randomized clinical trial.3 ** Avoid co-prescribing a DPP-4i and GLP-1 RA because they act through overlapping mechanisms.
- Each time a medication is added or adjusted, reinforce diet and exercise, assess adherence to current medications, and optimize doses.
- Add additional medications if needed to achieve the patient’s HbA1c goal and/or reduce the risk of end-organ damage.
- Optimize treatment with multiple non-insulin options before adding insulin.
Additional Resources for Providers
- Find Certified Diabetes Educators in Pennsylvania
- ADA Recognized Education Programs
- Accredited American Association of Diabetes Educators Programs
Additional Resources for Patients
- ADA Type 2 Diabetes Basics
- ADA Living with Type 2 Diabetes Program
- CDC Diabetes Basics
- CDC Managing Diabetes
Information current at time of publication, May 2022.
The content of this website is educational in nature and includes general recommendations only; specific clinical decisions should only be made by a treating clinician based on the individual patient’s clinical condition.
References
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report website. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html. Accessed April 14, 2022.
-
Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, et al. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S1-S258.
- Lam CSP, Ramasundarahettige C, Branch KRH, et al. Efpeglenatide and Clinical Outcomes With and Without Concomitant Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibition Use in Type 2 Diabetes: Exploratory Analysis of the AMPLITUDE-O Trial. Circulation. 2022;145(8): 565-574.